Interstitial Cells of Cajal
- Published13 Nov 2020
- Author Calli McMurray
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
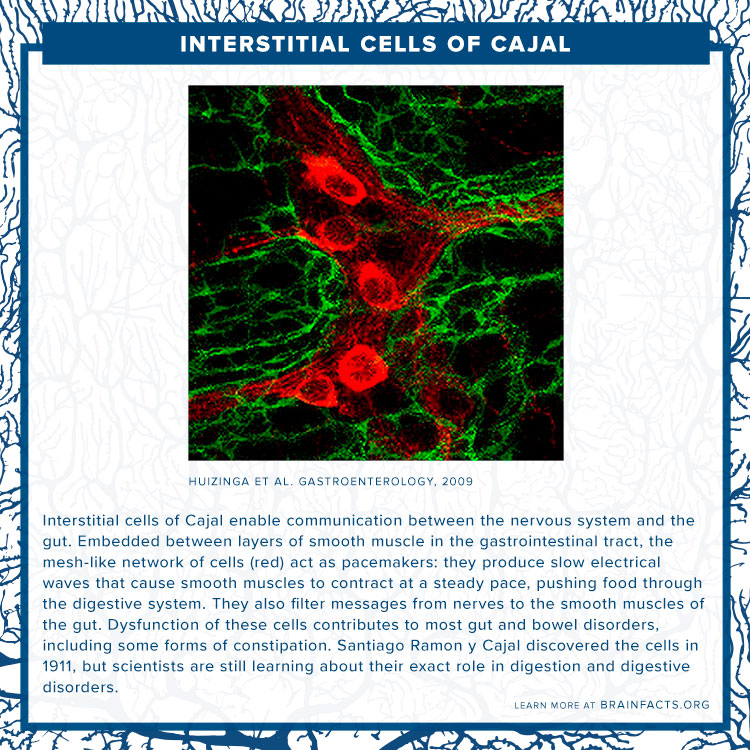
The gut’s pacemaker cells, interstitial cells of Cajal, produce slow electrical waves to keep food moving through the digestive tract.
Brain Bytes showcase essential facts about neuroscience.
Design by Adrienne Tong.
Image "Physiology, Injury, and Recovery of Interstitial Cells of Cajal" by Huizinga et al. Gastroenterology, 2009.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
References
Huizinga, J. D., Chen, J., Mikkelsen, H. B., Wang, X., Parsons, S. P., & Zhu, Y. F. (2013). Interstitial cells of Cajal, from structure to function. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7. doi:10.3389/fnins.2013.00043
Al-Shboul, O. A. (2013). The Importance of Interstitial Cells of Cajal in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 19(1), 3-15. doi:10.4103/1319-3767.105909
Huizinga, J. D., Zarate, N., & Farrugia, G. (2009). Physiology, Injury, and Recovery of Interstitial Cells of Cajal: Basic and Clinical Science. Gastroenterology, 137(5), 1548-1556. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.023
Klein, S., Seidler, B., Kettenberger, A., Sibaev, A., Rohn, M., Feil, R., . . . Saur, D. (2013). Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave activity. Nature Communications, 4(1). doi:10.1038/ncomms2626
Also In Cells & Circuits
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org