Understanding Brain Biochemistry Through Chemical Messengers
- Reviewed9 Mar 2023
- Author Susan Rojahn
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
Although we typically talk a lot about the electrical signals transmitted along neurons, the brain also communicates with molecular and chemical signals.
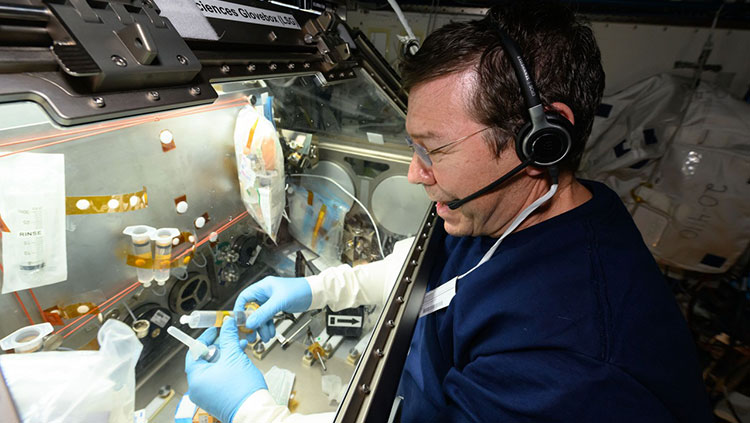
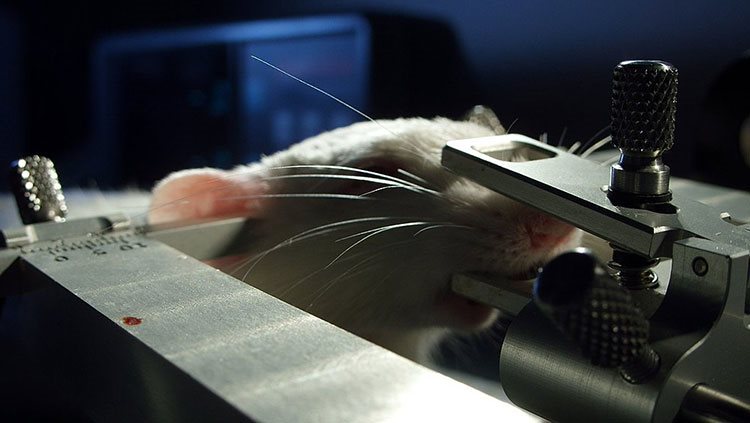
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that travel across a synapse, carrying signals from one neuron to the next. Using a method called microdialysis, researchers can monitor neurotransmitters in action. With thin tubes inserted into the brain, scientists can collect tiny volumes of liquid from just outside neurons and then analyze the compounds in that liquid. For example, a researcher could analyze liquid captured during learning to identify molecules that are important for that process.
Microdialysis can also be used to deliver compounds to the brain. Many drugs have powerful effects on the brain, so scientists can use these substances to tweak brain function in order to understand it better. Pharmacology, the study of the effects of drugs, is also dedicated to identifying new drugs to treat conditions like pain or psychiatric illness, as well as understanding addiction and other negative consequences of drug use.
Another important method employed to study the molecules and chemicals at work in the brain is mass spectrometry. Once a sample has been collected — perhaps by using microdialysis — the compounds it contains are ionized (given an electric charge) and then sent through an electric or magnetic field. The behavior of each molecule in that field indicates its mass. That information alone provides valuable clues for identifying a molecule. Mass spectrometry has also been very useful in exploring neurodegenerative disorders. For example, one treatment for Parkinson’s disease causes severe side effects, including involuntary movements. With mass spectrometry, researchers have identified the location within the brain where this side effect is caused; that information could point the way to interventions that can reduce or prevent those side effects.
Adapted from the 8th edition of Brain Facts by Susan Rojahn.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
References
Bao, W., Jia, H., Finnema, S., Cai, Z., Carson, R. E., & Huang, Y. H. (2017). PET Imaging for Early Detection of Alzheimer's Disease: From Pathologic to Physiologic Biomarkers. PET clinics, 12(3), 329–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpet.2017.03.001
Berman, M. G., Jonides, J., & Nee, D. E. (2006). Studying Mind and Brain with fMRI. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 1(2), 158–161. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsl019
Bögershausen, N., & Wollnik, B. (2013). Unmasking Kabuki syndrome. Clinical genetics, 83(3), 201–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12051
Boyden E. S. (2015). Optogenetics and the Future of Neuroscience. Nature neuroscience, 18(9), 1200–1201. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4094
Caraci, F., Leggio, G. M., Salomone, S., & Drago, F. (2017). New Drugs in Psychiatry: Focus on New Pharmacological Targets. F1000Research, 6, 397. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.10233.1
Carter M. and Shieh J. C. (2015). Guide to Research Techniques in Neuroscience. Academic Press. p 164.
Carter N. P. (2007). Methods and Strategies for Analyzing Copy Number Variation Using DNA Microarrays. Nature genetics, 39(7 Suppl), S16–S21. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2028
Chefer, V. I., Thompson, A. C., Zapata, A., & Shippenberg, T. S. (2009). Overview of Brain Microdialysis. Current protocols in neuroscience, Chapter 7, Unit 7.1. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0701s47
Clancy, S. (2008). Copy Number Variation. Nature Education, 1(1):95. https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/copy-number-variation-445/
Cohen M. X. (2017). Where Does EEG Come From and What Does It Mean?. Trends in neurosciences, 40(4), 208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2017.02.004
Courtney, K. E., & Ray, L. A. (2014). Methamphetamine: An Update on Epidemiology, Pharmacology, Clinical Phenomenology, and Treatment Literature. Drug and alcohol dependence, 143, 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.08.003
Cui, X., Bray, S., Bryant, D. M., Glover, G. H., & Reiss, A. L. (2011). A Quantitative Comparison of NIRS and fMRI Across Multiple Cognitive Tasks. NeuroImage, 54(4), 2808–2821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.069
Flagel, S. B., Chaudhury, S., Waselus, M., Kelly, R., Sewani, S., Clinton, S. M., Thompson, R. C., Watson, S. J., Jr, & Akil, H. (2016). Genetic Background and Epigenetic Modifications in the Core of the Nucleus Accumbens Predict Addiction-like Behavior in a Rat Model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(20), E2861–E2870. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1520491113
Gratten, J., Wray, N. R., Keller, M. C., & Visscher, P. M. (2014). Large-scale genomics unveils the genetic architecture of psychiatric disorders. Nature neuroscience, 17(6), 782–790. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3708
Hämäläinen, M., Hari, R., Ilmoniemi, R. J., Knuutila, J., & Lounasmaa, O. V. (1993). Magnetoencephalography—Theory, Instrumentation, and Applications to Noninvasive Studies of the Working Human Brain. Reviews of modern Physics, 65(2), 413. https://journals.aps.org/rmp/abstract/10.1103/RevModPhys.65.413
Hanrieder, J., Phan, N. T., Kurczy, M. E., & Ewing, A. G. (2013). Imaging Mass Spectrometry in Neuroscience. ACS chemical neuroscience, 4(5), 666–679. https://doi.org/10.1021/cn400053c
Heather, J. M., & Chain, B. (2016). The Sequence of Sequencers: The History of Sequencing DNA. Genomics, 107(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2015.11.003
Heidenreich, M., & Zhang, F. (2016). Applications of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Neuroscience. Nature reviews. Neuroscience, 17(1), 36–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2015.2
Herbst, S. M., Proepper, C. R., Geis, T., Borggraefe, I., Hahn, A., Debus, O., Haeussler, M., von Gersdorff, G., Kurlemann, G., Ensslen, M., Beaud, N., Budde, J., Gilbert, M., Heiming, R., Morgner, R., Philippi, H., Ross, S., Strobl-Wildemann, G., Muelleder, K., Vosschulte, P., … Hehr, U. (2016). LIS1-associated Classic Lissencephaly: A Retrospective, Multicenter Survey of the Epileptogenic Phenotype and Response to Antiepileptic Drugs. Brain & development, 38(4), 399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.braindev.2015.10.001
Hopf, F. W., & Lesscher, H. M. (2014). Rodent Models for Compulsive Alcohol Intake. Alcohol (Fayetteville, N.Y.), 48(3), 253–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.03.001
Johnson, A. C., & Greenwood-Van Meerveld, B. (2016). The Pharmacology of Visceral Pain. Advances in pharmacology (San Diego, Calif.), 75, 273–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2015.11.002
Kandel, E. R., Dudai, Y., & Mayford, M. R. (2014). The Molecular and Systems Biology of Memory. Cell, 157(1), 163–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.001
Lee, G. J., Park, J. H., & Park, H. K. (2008). Microdialysis Applications in Neuroscience. Neurological research, 30(7), 661–668. https://doi.org/10.1179/174313208X289570
Leroy, A., Foucher, J. R., Pins, D., Delmaire, C., Thomas, P., Roser, M. M., Lefebvre, S., Amad, A., Fovet, T., Jaafari, N., & Jardri, R. (2017). fMRI Capture of Auditory Hallucinations: Validation of the Two-Steps Method. Human brain mapping, 38(10), 4966–4979. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23707
Liu, Z., Ding, L., & He, B. (2006). Integration of EEG/MEG with MRI and fMRI. IEEE engineering in medicine and biology magazine : the quarterly magazine of the Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society, 25(4), 46–53. https://doi.org/10.1109/memb.2006.1657787
Lodish H., Berk A., Zipurksy S. L. et. al., editors. (2000). Molecular Cell Biology, 4th edition. Freeman, p 94, 140, 147-148, 268-269.
Malik, A. N., Vierbuchen, T., Hemberg, M., Rubin, A. A., Ling, E., Couch, C. H., Stroud, H., Spiegel, I., Farh, K. K., Harmin, D. A., & Greenberg, M. E. (2014). Genome-wide Identification and Characterization of Functional Neuronal Activity-Dependent Enhancers. Nature neuroscience, 17(10), 1330–1339. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3808
Mayford, M., Siegelbaum, S. A., & Kandel, E. R. (2012). Synapses and Memory Storage. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 4(6), a005751. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a005751
Maze, I., Shen, L., Zhang, B., Garcia, B. A., Shao, N., Mitchell, A., Sun, H., Akbarian, S., Allis, C. D., & Nestler, E. J. (2014). Analytical Tools and Current Challenges in the Modern Era of Neuroepigenomics. Nature neuroscience, 17(11), 1476–1490. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3816
National Human Genome Research Institute. (July 2017). An Overview of the Human Genome Project. Accessed July 17, 2017 at https://www.genome.gov/12011238/an-overview-of-the-human-genome-project/
National Institute of Mental Health. (2017). Brain Stimulation Therapies. Accessed July 17, 2017 at https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/brain-stimulation-therapies/brain-stimulation-therapies.shtml
Olgiati, S., Quadri, M., & Bonifati, V. (2016). Genetics of Movement Disorders in the Next-Generation Sequencing Era. Movement disorders, 31(4), 458–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26521
Perry, R. H., Blessed, G., Perry, E. K., & Tomlinson, B. E. (1980). Histochemical Observations on Cholinesterase Activities in the Brains of Elderly Normal and Demented (Alzheimer-type) Patients. Age and ageing, 9(1), 9–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/9.1.9
Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, et al., editors. (2008). Neuroscience. 4th edition. Sinauer Associates, Inc. p 3-5, 16-17, 19-21, 25-27, 181-187, 465, 559, 673-674, 715-717.
Sejnowski, T. J., Koch, C., & Churchland, P. S. (1988). Computational Neuroscience. Science (New York, N.Y.), 241(4871), 1299–1306. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3045969
Sokolowski M. B. (2001). Drosophila: Genetics Meets Behaviour. Nature reviews. Genetics, 2(11), 879–890. https://doi.org/10.1038/35098592
Svoboda, K., & Yasuda, R. (2006). Principles of Two-Photon Excitation Microscopy and its Applications to Neuroscience. Neuron, 50(6), 823–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2006.05.019
Turek, F. W., Pinto, L. H., Vitaterna, M. H., Penev, P. D., Zee, P. C., & Takahashi, J. S. (1995). Pharmacological and Genetic Approaches for the Study of Circadian Rhythms in Mammals. Frontiers in neuroendocrinology, 16(3), 191–223. https://doi.org/10.1006/frne.1995.1007
US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. (2017). Genetics Home Reference – Huntington Disease. Accessed July 17, 2017 at https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/huntington-disease#genes
Usdin, K., & Kumari, D. (2015). Repeat-mediated Epigenetic Dysregulation of the FMR1 Gene in the Fragile X-related Disorders. Frontiers in genetics, 6, 192. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00192
Yoshino, K., Oka, N., Yamamoto, K., Takahashi, H., & Kato, T. (2013). Functional Brain Imaging Using Near-infrared Spectroscopy During Actual Driving on an Expressway. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 7, 882. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00882
What to Read Next
Also In Tools & Techniques
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org