Powering New Neurons
- Published30 May 2014
- Reviewed30 May 2014
- Author Michael W. Richardson
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
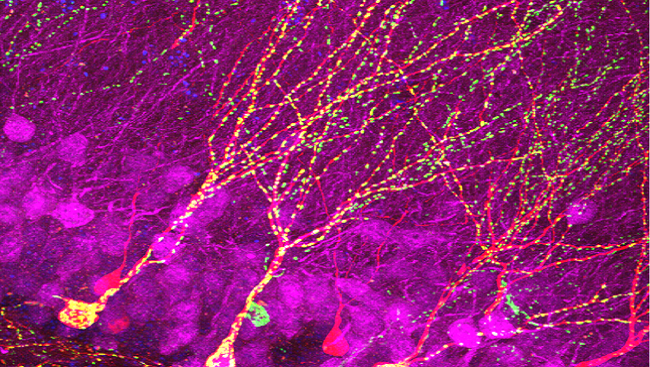
Image Credit: Steib, et al. The Journal of Neuroscience, 2014.
The hippocampus, a brain region involved in learning and memory, is one of only a few areas in the brain that continues to create new neurons throughout adulthood. In this image of a mouse hippocampus (magenta), new cells are labelled in red, and mitochondria— the intracellular power packs responsible for driving cellular activities throughout the body — are labelled in green. To better understand the role mitochondria play in cell growth, researchers tracked the changes that took place in the mitochondria of new cells as they grew under normal conditions or after animals were exposed to exercise.
They found that as fledgling cells in the hippocampus grow, the mitochondria undergo significant changes to support these cells. Specifically, exercise — which is already known to boost the creation of new neurons — increased the number and position of the mitochondria present in these cells, a key reminder of how behavior can affect ongoing brain development.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
Also In Brain Development
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org