There's No Eye in Team
- Published14 Aug 2017
- Reviewed13 Aug 2017
- Author Alexis Wnuk
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
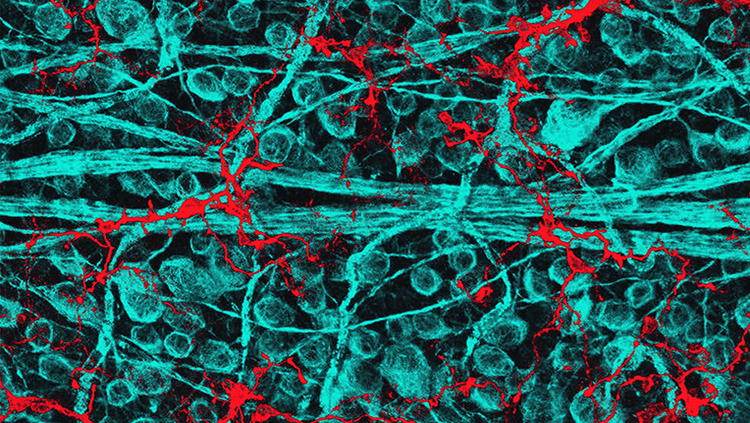
The retina is the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. It contains many different types of cells, each with a specific job to do. This magnified view of a mouse retina shows two types of cells found in the retina: retinal ganglion cells (light blue) send visual information from the eye to the brain, and immune cells called microglia (red) fight pathogens, clean up damaged cells, and help maintain connections between neurons.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
Also In Vision
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org