Grandma Chloe Gets Lost in Her Neighborhood
- Published20 Dec 2022
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
Memory loss is just one symptom of Alzheimer’s disease. Depression, anxiety, mood swings, and irritability can all be outward signs. Inside the brain, certain chemical changes cause abnormal structures, called tangles and plaques, to form. These structures disrupt normal function and communication between neurons. Those changes, along with inflammation, cause brain function to worsen over time, resulting in the progressive decline often seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
This is a video from the 2022 Brain Awareness Video Contest.
Created by Grace Osigbo.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
Transcript
Grandma Chloe can simply be described as a petite, jolly, and easy-going woman. She is 65, and she is my favorite grandma.
During the holidays, I visit her often where she reads me stories and shares jokes that makes me laugh hard. It was always fun with grandma. Recently, dad complained grandma was having mood swings. She was grumpy now, and the next minute, happy. She became easily irritated.
Two days ago, she was seen crying and complaining to a neighbor that she didn't know where she was. In her words, "she was lost." How could this be? Lost in the same neighborhood she had lived for over 20 years?
We took her to the hospital, and after several tests and interactions with the doctor, the doctor told my dad that she had Alzheimer’s. Now, I made some research, and I found out that Alzheimer is a neurodegenerative disease of the brain that is progressive.
It was discovered by the German psychiatrist, Alois Alzheimer in 1906. It has the following symptoms:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Mood swings
- Distrust in others
- Memory loss
- Wandering
- Irritability
How does this occur? How does it develop? It begins from the brain.
The brain is broadly divided into three: The cerebral hemispheres that initiate and control voluntary movement, regulate thoughts, and mental activity such that deals with numbers like arithmetic; the cerebellum that maintains balance and posture; the brain stem that connects the spinal cord and the brain, houses the medulla oblongata that controls involuntary processes like heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure. The hippocampus is a complex brain structure embedded deep in the temporal lobe of the cerebral hemispheres. It plays a major role in learning and memory and is most affected by Alzheimer's disease.
Neurons are the fundamental unit of the brain and nervous system. They receive sensory input from the external world, external environment, process it, send motor commands to our muscles, and relays the electrical signals to other neurons at every step in between. For neurons to function, they must communicate with each other, perform metabolism, and undergo regeneration. Now Alzheimer's disease disrupts this.
Scientific research has revealed some of the brain changes that occur in Alzheimer's disease. Abnormal structures such as amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles are the biological hallmark of the disease.
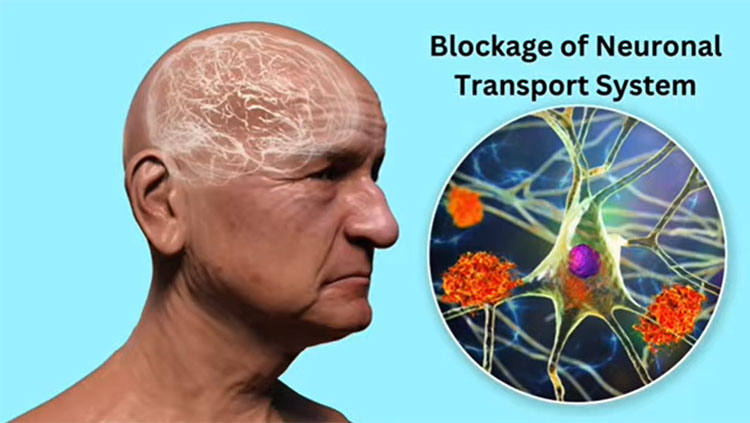
Now, microtubules are internal structures that support neurons. They help in the delivery of nutrients and molecules from the cell body to the other parts of the neurons. Tau proteins are specialized proteins that bind to and stabilize microtubules in the brain.
In Alzheimer’s, abnormal chemical changes called hyperphosphorylation cause tau proteins to detach from microtubules, stick to each other forming spirals that further assemble to form tangles. These tangles intercept with the basic function of the neurons, and with time, neurons die.
Let's look at the formation of amyloid plaques. APP molecule known as Amyloid Precursor Protein is a transmembrane protein that is expressed at high levels in the brain. It helps neurons grow and repair.
It is metabolized by these enzymes: alpha, beta, and gamma secretases. Its metabolism occurs in a sequence. The normal sequence is alpha and gamma, but in Alzheimer’s the sequence is beta and gamma. This produces beta-amyloid proteins that are not soluble, have 36-43 amino acids; they are sticky and toxic. Now they bind together to form plaques that can get in between the neurons and prevent them from communicating.
Other pathological changes like inflammation, together with these processes mentioned, cause continuous cell death. As the cells die starting from the hippocampus, memory is affected, other parts of the brain follow; the functions of these parts are halted. With time, the overall functioning of the brain becomes affected as seen in the severe stage of the disease.
Now that's a summary of how Alzheimer's disease occur and progress. Thank you for listening!
Also In Alzheimer's & Dementia
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org